
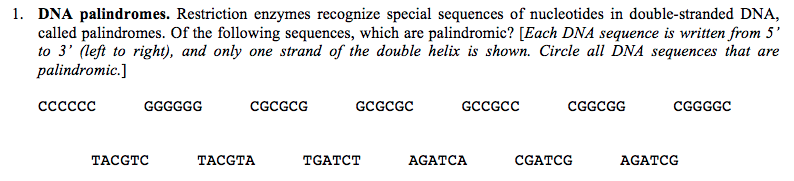
It will also discuss the applications of restriction enzymes in molecular biology and biotechnology and the potential limitations when working with these enzymes. This article will provide information about restriction enzymes, their properties, classification and action mechanisms. The discovery of restriction enzymes helped revolutionize the field of molecular biology by giving scientists the ability to manipulate DNA and study it in various applications including genetic engineering and DNA sequencing. Restriction enzymes are proteins produced by bacteria and archaea that can cleave DNA molecules at specific sites to create DNA fragments that have known sequences at each end. Type I, Type III and Type IV have more complex mechanisms of action and are less commonly used in research. It recognizes and cuts DNA at specific palindromic sequences, resulting in DNA fragments with sticky ends that can be easily ligated to other DNA fragments. Type II is the most commonly used in molecular biology research. The four types of restriction enzymes are Type I, Type II, Type III and Type IV. HALO® Chromatography Columns and Consumables+. Sartorius laboratory instruments, consumables and services PerkinElmer - Innovating for a Healthier World Lab Thermometers & Temperature Measurement EquipmentĪgilent Chemistries and Supplies Portfolio Quality Products from Sheldon Manufacturing Life Science Research Solutions, Products, and Resources VWR will support you from the latest life science products to the guaranteed purity of organic building blocks. Moreover, even very few examples that we have examined so far indicate the importance of further studies on protein palindromes.A strong, vibrant research and development group is the lifeblood of all industries. Our results have clearly showed that palindromes are frequently occurring motives in proteins. As the number of possible palindromic sequences of a given length is far much greater for proteins (20N) than for nucleic acids (4N), the study on their role seems to be an exciting challenge. Oligonucleotide LTI-ITL has been observed in the crystal structure and is located close to a DNA recognizing domain. The other palindrome containing protein is cellular human tumor suppressor p53. It contains palindrome in its beta-sheet domain that interacts with palindromic fragment of DNA. One example of such protein is systemin, an 18-amino-acid-long peptide. A great number (26%) of different protein palindromes were found. One can ask the questions, Do palindromes occur in protein, and if so, what function they play? We have searched the protein SWISSPROT database for palindromic sequences. Palindromes in telomeres are crucial for initiation of replication. For example, restriction enzymes often recognize palindromic sequences of DNA. They occur in genomes of all organisms and have various functions. Palindromes in DNA consist of nucleotides sequences that read the same from the 5'-end to the 3'-end, and its double helix is related by twofold axis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
